
Polymers, Free Full-Text
4.8 (625) In stock

4.8 (625) In stock
Water transfer through porous textiles consists of two sequential processes: synchronous wicking–evaporating and evaporating alone. In this work we set out to identify the main structural parameters affecting the water transfer process of cotton fabrics. Eight woven fabrics with different floats were produced. The fabrics were evaluated on a specially designed instrument capable of measuring the water loss through a vertical wicking process. Each test took 120 min, and two phases were defined: Phase I for the first 10 min and Phase II for the last 110 min according to wicking behavior transition. Principal components and multivariate statistical methods were utilized to analyze the data collected. The results showed that Phase I dominated the whole wicking–evaporating process, and the moisture transfer speed in this phase varied with fabric structure, whereas the moisture transfer speeds in Phase II were similar and constant regardless of fabric structure. In addition, fabric with more floats has high water transfer speed in Phase I due to its loosened structure with more macropores.

Polymers, Free Full-Text, Resin Curing

Polymers, Free Full-Text
Polymers, Free Full-Text
Polymers, Free Full-Text, pla cf

Polymers, Free Full-Text, pla cf
Polymers, Free Full-Text
køn Bær skøjte polycarbonate glass transition fejl skrot begå

Polymers, Free Full-Text
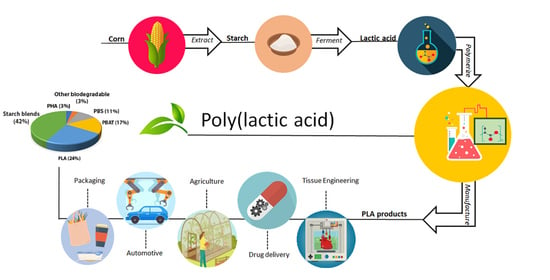
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Polymers, Free Full-Text, nmm2 values

Polymers, Free Full-Text

Polymers, Free Full-Text
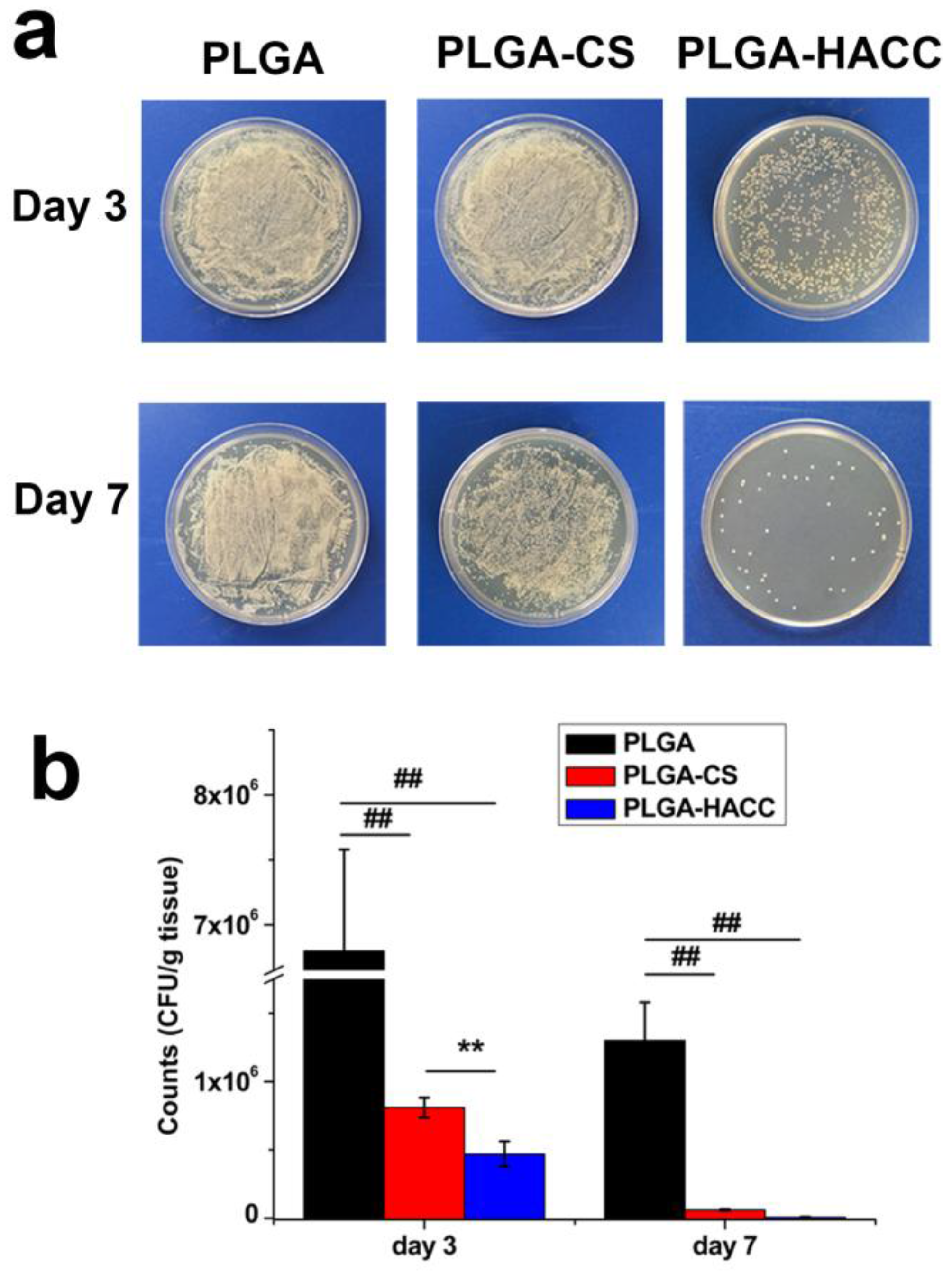
Polymers, Free Full-Text, Polyester Dye

Polymers, Free Full-Text, nmm2 values