
Postmenopausal bleeding (Pmb) and benign conditions Study in rural
5 (272) In stock

5 (272) In stock
Detailed history Assessment of risk factors Full clinical examination Investigations: Routine Pap smear Appropriate biopsy Smear Cytology TVS HSG combined with TVS Saline sono-hysterography CT MRI (as required)
Postmenopausal bleeding (Pmb) and benign conditions Study in rural belt of India
Benign conditions though most frequent and can cause considerable distress. Study: In Gynecology department, RIMS, a rural based tertiary center (Jan’10-July’12) patients, 1200 Pmb. Aim To exclude malignancy To confirm diagnosis To treat accordingly.
Para<=5: 513 (57 %) Low SES: 700 (78%) No circumcision: 555 (61.66%) belonging to Hindu community
50-54 yrsEndometrial (Em) yrs Endometrial (Em)
300(25%) in present study had malignant lesions. Community education, mass screening, regular follow up, timely intervention is necessary even with slight bleeding. Em. Thickness >4mm, bulky uterus considered malignant unless until proved..
QUESTIONS Thank you Dr Gopa Chowdhury Asstt. Prof, RIMS, Ranchi INDIA
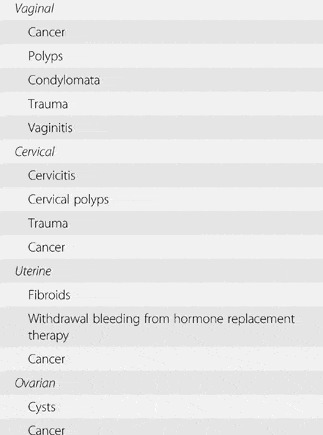
Genitourinary concerns (Section 3) - Handbook of Women's Health
Post Menopausal Bleeding - Torbay PCT

Postmenopausal Bleeding: An Update European Journal of Medical and Health Sciences

Post-menopausal bleeding PV Dr Nasira Sabiha Dawood. - ppt download

Postmenopausal bleeding (Pmb) and benign conditions Study in rural belt of India. - ppt download
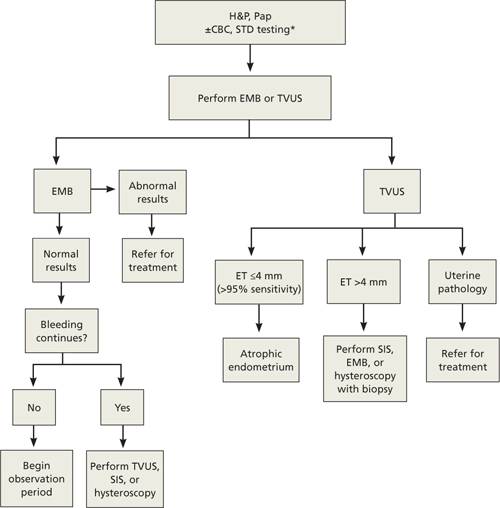
Postmenopausal bleeding: First steps in the workup
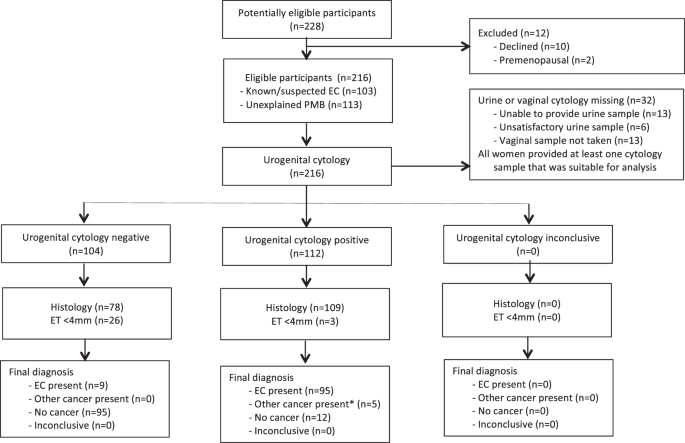
Diagnostic accuracy of cytology for the detection of endometrial cancer in urine and vaginal samples

Postmenopausal bleeding (Pmb) and benign conditions Study in rural belt of India. - ppt download

Postmenopausal Bleeding among Rural Women in Tamil Nadu, India: Mixed Methods Study. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Genitourinary concerns (Section 3) - Handbook of Women's Health