
Temperature & Heat Warm- up Define Kinetic energy (KE) - ppt download
4.6 (321) In stock

4.6 (321) In stock
solution Kinetic energy is the energy of motion Moving motor bike has kinetic energy A running person has KE
Temperature & Heat Warm- up Define Kinetic energy (KE)
____________________________. The KE formula is:_____________. Calculate the kinetic energy of a 3 kg toy car that moves at 4m/s. _____________________________.
Moving motor bike has kinetic energy. A running person has KE.
solution KE = ½ mv2 ½ (3)(42) 24Joules
Temperature & Heat Define temperature:___________________________________________________
scale. Freezing point. Boiling point. Fahrenheit. 32º F. 212º F. Celsius. 0º C. 100º C. Kelvin. 273 K. 373 K.
The American Meteorological department prefer using Fahrenheit scale to Celsius scale in their weather reports because___________________________________________________________________.
What is the relationship between temperature and Kinetic Energy of molecules Solution: The greater the temperature, the greater the Kinetic energy of the particles (molecules) of the object.
Conversion formula. F= Temperature in Fahrenheit. C = Temperature in Celsius. K = Temperature in Kelvin.
problem Convert 30 0c to Fahrenheit Solution=
Convert 89 ºF into. a) Celsius and. b) Kelvin. Textbook Pg 322 # 1-5.
2. How many joules of work are done on an object when a force of 10 N pushes it a distance of 10 m _________________________________.
Just as work, heat is a form of energy transfer between systems.
For heat to be transferred from cold to hot, external work has to be done. Example. External work is done to cool homes ( Air conditioning) Without air conditioning, Heat from outside environment gets into the house to raise the temperature of the house.
Thermal contact: ___________. Thermal equilibrium: ________.
The molecules of every substance, whether solid, liquid or gas are in perpetual motion. If heat is supplied to a substance, the motion (the vibration) of its molecules increases as its temperature rises. The kinetic energy of the molecules therefore increases. Thus heat is a form of energy. Thermal contact: -when heat gets transferred between objects that are in contact. Thermal equilibrium :-when two objects at different temperatures come into contact and heat gets transferred to the cooler object such that there is no more temperature difference.
You heat a half cup of tea and its temperature rises by 40C. How much will the temperature rise if you add the same amount of heat to a full cup of tea When a hot object cools down, where does the energy go
Answer By 20C The energy is used to heat up the surrounding.
Internal energy is the sum total of potential and kinetic energy of the individual particles of a body.____. Heat content of a body is the same as temperature.____. Heat content of a body is always transferred._____.
This is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 10C. Kilocalorie is 1000 calories: - is heat required to raise 1 kg of water by 10C. Calorie ( with capital ‘C’)- the Food unit is actually a Kilocalorie.
converting calorie to joule. 1 calorie = joules. 1 kilocalorie = 4184 joules.
Specific heat capacity is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of a Unit mass of a substance by 1º C. Specific heat capacity of water is : calories. Joules. For 1 gram of water. 1 cal/g0C J/g0C. For 1kg of water cal/kg0C J/kg0C.
Substance. Specific Heat Capacity at 25oC in J/goC. Hydrogen gas Helium gas water lithium ethyl alcohol ice at 0oC steam at100oC. vegetable oil air magnesium. aluminum Concrete glass potassium
The factors to consider when quantifying the amount of heat transferred into a substance are: Mass (m), Change of temperature (ΔT), and. Specific heat capacity ( c ). Quantity of heat Q = mc ΔT.
Soln: Q = mc ΔT. a) Q = 1 x 4184x 45 = __________. b) Q = 1 x 1000 x 45 = __________.
Class work/ Homework Textbook pg 322 # 6-12 Textbook Page: 323 # 19-24
change in length = (original length) • (coefficient of expansion)• (change in temperature) Example: If a 20 cm iron rod whose coefficient of expansion is 12 x 10-60/C is heated to a temperature of 400C from room temperature of about 230C, What is its change in length
Whenever two substances at different temperatures and mixed, the hot one cools down while the cold one warms up. However; Heat Lost = Heat Gained.
Example: What would be the final temperature if you mixed 3 liters of water at 300C and 2 liters of water at 500C
Class work Textbook Page 324, # 40-48,
Objective. Use the formula for quantity of heat. Q = m · c · ΔT to solve problems on heat. Use the concept of heat lost by an object = Heat gained by another object to solve heat problems.
What is the heat lost by a 500 ml (500 g) water at 100º C when put in a fridge at 15º C Specific heat capacity of water is J/g·º C.
Class work: Workbook pg 144 exercises 8 –11 Page 147 # A8-A10

Temperature & Heat Warm- up Define Kinetic energy (KE) - ppt download

Heat Transfer – Conduction, Convection and Radiation

Temperature & Heat Warm- up Define Kinetic energy (KE) - ppt download
OverviewLooking for a way to teach environmental science while providing students with an opportunity to use their newfound skills in the virtual and

Kinetic Energy, Heat, and Temperature Presentation
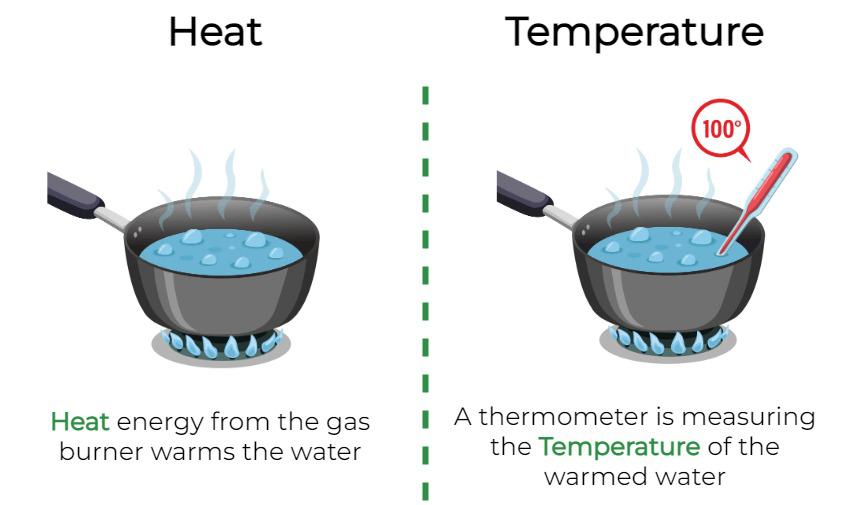
Difference Between Heat and Temperature - SI Unit, Measurement, FAQs

Exploring Kinetic Energy - Types, Examples, Formula Derivation
Thermal Energy Movement Teaching Slides

Heat Transfer - PowerPoint Slides - LearnPick India

Heat and Temperatures PowerPoint (teacher made) - Twinkl

Materials, Free Full-Text

What is Heat, Specific Heat & Heat Capacity in Physics? - [2-1-4

Emerging trends in metal-organic framework (MOFs) photocatalysts
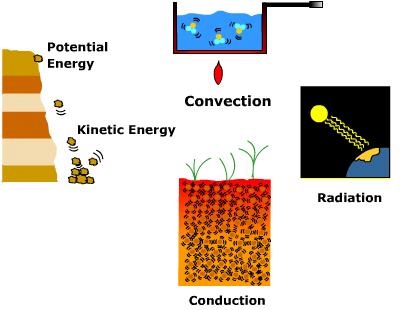
4.1: Energy and Heat - Geosciences LibreTexts

Energy in Earth Processes Learning Activities (Distance Learning)

Ch 5 Thermal Energy and Heat - general.ppt