
The role of the gastrointestinal barrier in obesity‐associated systemic inflammation - Acciarino - Obesity Reviews - Wiley Online Library
4.9 (748) In stock

4.9 (748) In stock

PDF) Increased jejunal permeability in human obesity is revealed by a lipid challenge and is linked to inflammation and type 2 diabetes: Jejunal permeability in human obesity

Overcoming the intestinal barrier: A look into targeting
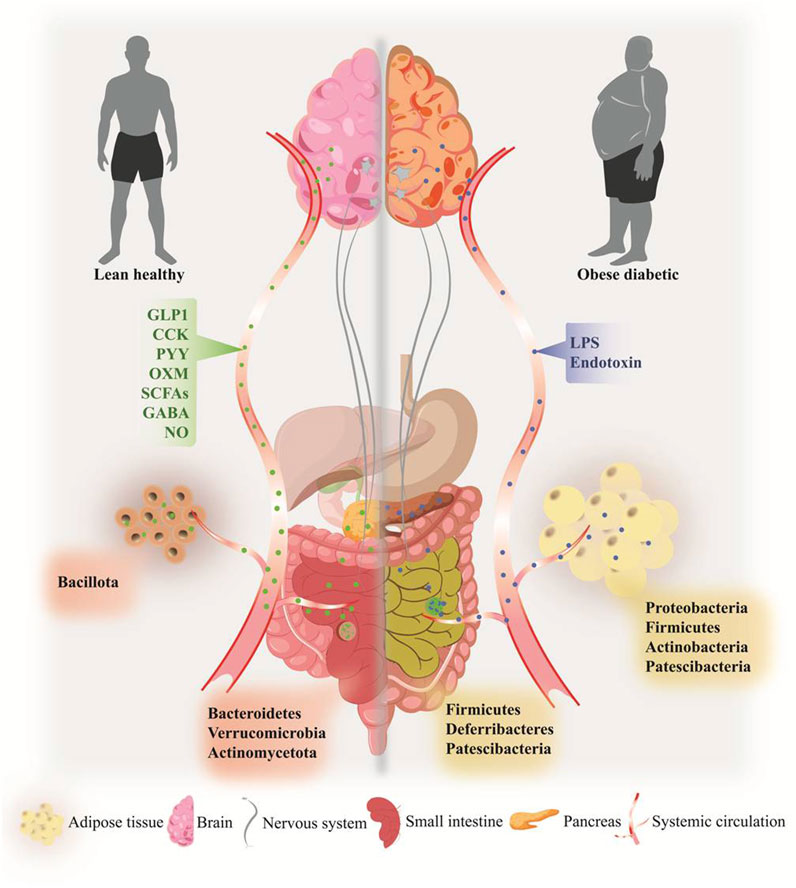
Frontiers Recent insights of obesity-induced gut and adipose tissue dysbiosis in type 2 diabetes
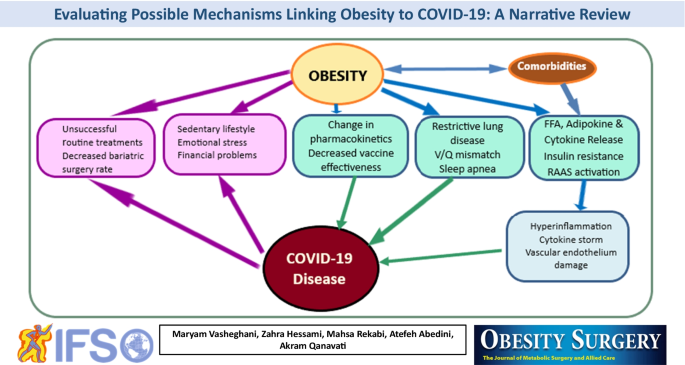
Evaluating Possible Mechanisms Linking Obesity to COVID-19: a Narrative Review

PDF) Role of Overweight and Obesity in Gastrointestinal Disease

Obesity is linked to several diseases including cardiovascular disease
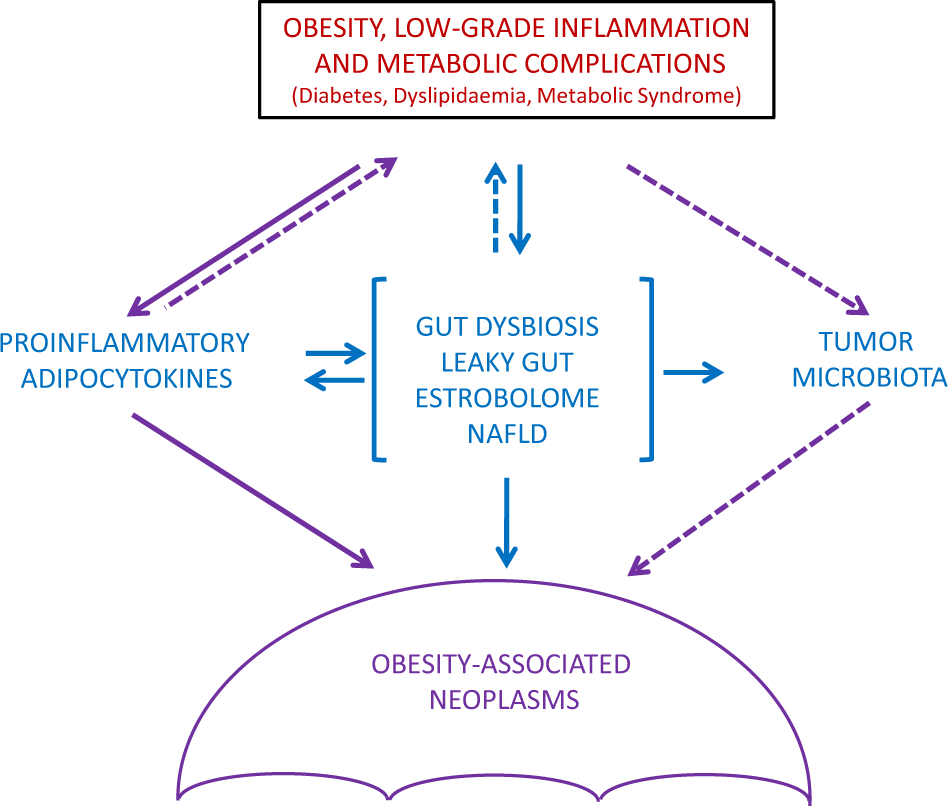
Spot-light on microbiota in obesity and cancer

PDF) Psychological stress and corticotropin-releasing hormone increase intestinal permeability in humans by a mast cell-dependent mechanism

Frontiers Intestinal Barrier Function and Immune Homeostasis Are Missing Links in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Development
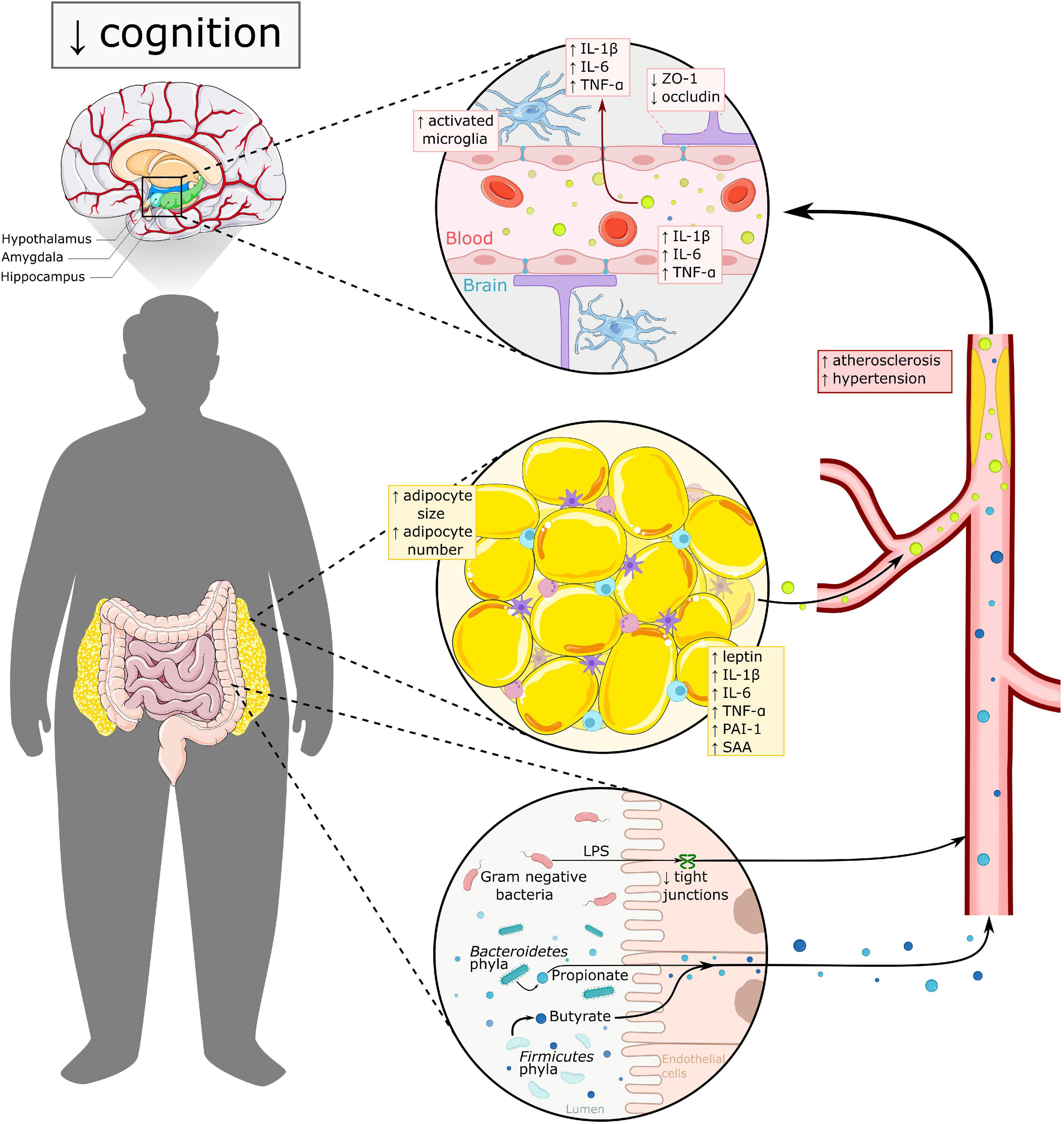
Frontiers Gut Microbiome, Inflammation, and Cerebrovascular Function: Link Between Obesity and Cognition

PDF) Inflammatory Signatures of Maternal Obesity as Risk Factors for Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Role of Maternal Microbiota and Nutritional Intervention Strategies
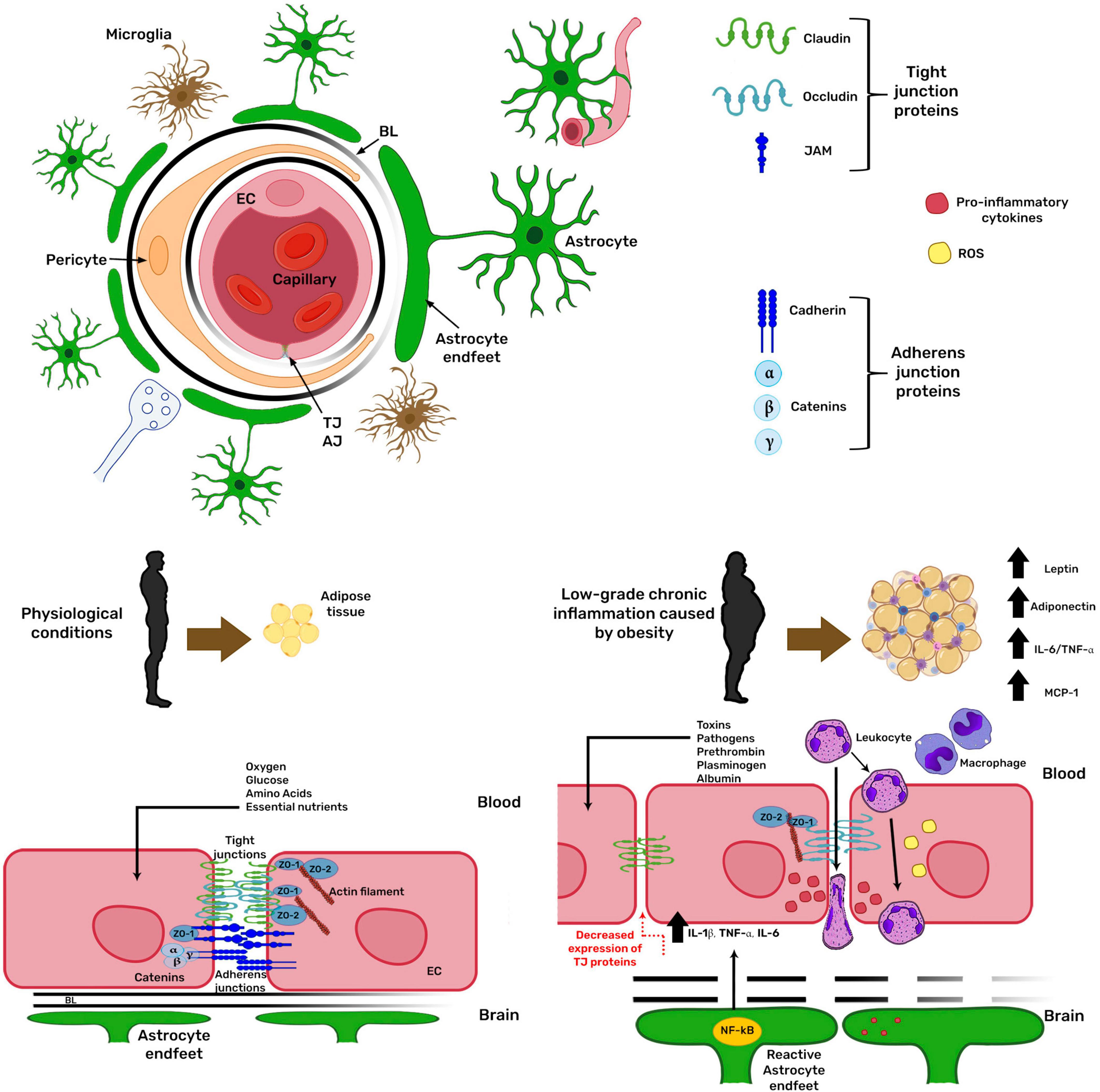
Frontiers The Obese Brain: Mechanisms of Systemic and Local

Gut microbiota-mediated inflammation in obesity: a link with gastrointestinal cancer